Every once in a while we receive a request for a printable manual for Kairatune.
Kairatune 1.2 Reference ManualKairatune Video Manual
There’s a new video manual for Kairatune available by Nick Maxwell from Nick’s Ableton Live Tutorials.

[Update: all Nick’s stuff has gone offline]
Kairatune advanced features
Preset manager

The preset manager has some features that are only accessible by right-clicking on the preset list.
- Details option displays a preset detail editor that lets you modify the preset name and category and add other supplemental information to the preset. Double clicking on a preset name also displays the detail editor.
- Copy and Paste options lets you duplicate and copy a preset across instances of Kairatune. The Paste option always appends the set of presets instead of replacing the current preset.
- New option simply adds a new preset with default parameter values and with the name “Init”.
- Export option lets you save the preset as a ktpreset file.
- Remove option simply removes the preset.
- MIDI assignments sub menu lets you copy, paste or clear the MIDI assignments of the current preset.
Plugin configuration

The button on the upper right corner opens a configuration menu. Through the configuration menu you can load or import presets from various file types and export the current set of presets as a ktbank file.
- Load option replaces the current set of presets.
- Import option appends the current set of presets.
You can import ktpreset single preset files and load or import ktbank preset bank files exported from Kairatune version 1.2. You can import single preset FXP files and load or import FXB preset bank files generated with prior versions of Kairatune.
- Restore factory presets replaces the current set of presets with the built in presets.
- Remove all presets option clears the current set of presets.
If you want Kairatune to start up with a custom set of presets, you can configure the current set to anything you want and set that as the default. After you’ve set the default, any new Kairatune instances will launch with the new default set of presets.
MIDI learn
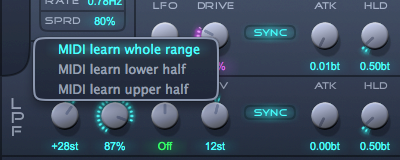
The MIDI learn menu opens by right-clicking on a control. The menu provides options for assigning a MIDI controller to the parameter by learning. In short, MIDI learning means that you instruct Kairatune to listen to MIDI controllers and assign the first controller it receives to control the selected parameter. The three different variations let you assign the control to the specified sub ranges of the parameter’s values.

After you’ve assigned a controller you will see a separate sub menu for each assigned controller. The sub menu provides options to further modify the controller range or remove the assignment.
Signal flow
I was asked about the signal flow of the synth. Since the GUI doesn’t really reflect the signal flow within the sound engine, i’d better just put out a graph.

As you can see the pitch module isn’t included. The pitch module produces only a control signal that is used by many modules in different ways.
Sound engine overview
Kairatune’s sound engine consists of
- generator section,
- pitch section,
- spread section,
- amp section,
- filter section and
- effects section.
Generator
The generator section has just one multi-oscillator. The basic waveform generator is very simple adjustable mix of sawtooth and square wave. The multi-oscillator generates five waveforms whose relative pitch, phase and amplitude may be configured and modulated enabling a rich set of tones. The multi-oscillator uses quite unusual technique that generates a single fundamental signal independently of the (multiple) overtones, preventing the beating effect that arises where several oscillators are output in slightly detuned unison, yet preserving the full and fat sound on the overtone spectrum. The method enables building very rich and full sounds on a perfectly solid bottom and is especially useful in creating tight bass and low register lead sounds.
Pitch
The pitch can be modulated by a traditional vibrato, by a trill modulator and by a shared (sinewave) LFO source. The trill modulator is basically a square wave LFO. The modulation depth of all three modulators is independently controllable by an envelope. This enables the momentary use of quite extreme modulation. With the modulation envelopes the exact time and duration of the modulation can be set to produce some quite interesting effects and timbres.
Spread
The spread section makes the sound appear to oscillate in the stereo field. It uses a variable amount of high frequency damping and delay to create the illusion of movement.
Amp
The amp section modulates the amplitude by an AHDSR envelope and the shared LFO source and velocity. The asymmetric waveshaper can handle quite extreme driving without audible aliasing.
Filters
The filters section has a resonant lowpass filter and a resonant highpass filter. The cutoff frequency can be modulated independently by an AHDSR envelope and the shared LFO source. The lowpass filter’s cutoff frequency can be modulated by a spread modulator, which creates interesting effect in the stereo image, especially on high resonance configuration.
Effects
The effects section runs two delay units in parallel. One has a pre highpass filter and the other has a bandpass filter in the feedback chain. The cutoff frequency of the BPF is modulated by an dedicated LFO. The BPF delay is capable of some really interesting sounds on high feedback configuration. The effects section contains also a six stage phaser and two EQ units with selectable mode.